T lymphocytes constitute an important part of the adaptive immune system. The group led by Dr. Jose M. Rojo is interested in the basic mechanisms underlying the control of T lymphocyte activation, in particular, the study of the function of “costimulatory" molecules, like CD28 and ICOS, which are essential to the controlled modulation of immune responses.
Class IA Phosphoinositide-3 kinases (PI3K) bind to CD28 and ICOS and participate in normal activation of T lymphocytes. Now, in a work published in Frontiers in Immunology, the group of T lymphocyte activation has demonstrated that the catalytic subunit of PI3K, p110α, regulate antigen activation by T lymphocytes, an aspect previously neglected despite the relevance of this subunit in many cell types.
Class IA PI3K exists as different catalytic species. Specifically, the p110α isoform is ubiquitously expressed and has been the subject of extensive research oriented to cancer therapy due to its high rate of gain-of-function mutation in tumors, which is only equaled by KRas. However, its role in immune reactions has been shadowed by p110δ, another PI3K isoform preferentially expressed by lymphocytes and other leukocytes whose importance in T and B lymphocyte function and ontogeny, or in adaptive immunity is well established.
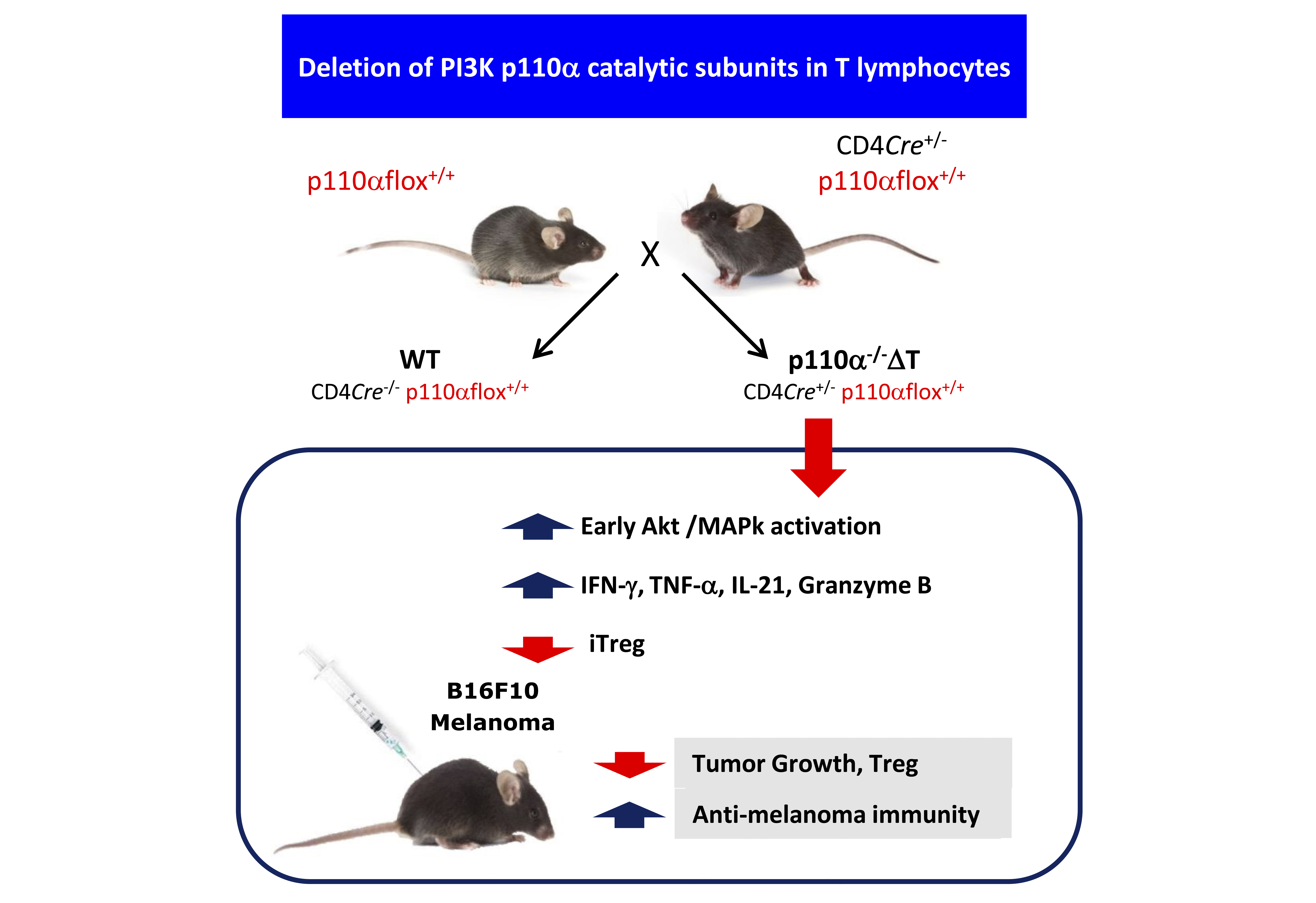
In previous works by the group, it was observed that the p110α isoform is as abundant in lymphocytes as p110δ, and like p110δ it can bind to and participate in the signals of costimulatory molecules like CD28 or ICOS. The new work by Aragoneses-Fenoll et al. was set out to further determine the importance of PI3K p110α in T cell function using mice with specific deletion of p110α.
Mice with deficiency of p110α in T lymphocytes were generated (named p110α-/-ΔT) which allowed demonstrating, firstly, a role for p110α in the homeostasis of CD4+ T cells which numbers are reduced. Furthermore, activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was enhanced. Other cytokines and effector molecules involved in the development of antibody responses, anti-virus and anti-tumor responses were increased in T helper lymphocytes or CD8+ effector cell from p110α-/-ΔT mice.
All these data suggest that p110α subunits at the same time participate and moderate PI3K signals during antigen activation of T lymphocyte and that the observed changed might favor immunity responses against tumors. Indeed, p110α-/-ΔT mice inoculated with B16.F10 melanoma showed delayed tumor progression and enhanced tumor-specific immune responses. This seems to suggest that the lymphocyte-specific deletion of p110α could be used to foster anti-tumor immunity.
Reference: T-cell specific loss of the PI-3 kinase p110a catalytic subunit results in enhanced cytokine production and anti tumor response. Aragoneses-Fenoll L, Ojeda G, Montes-Casado M, Acosta-Ampudia Y, Dianzani U, Portolés P, Rojo JM. Front Immunol 2018; 9: e332. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00332.

