Cells undergoing senescence present a characteristic stable cell cycle arrest; thus, senescence is considered to be an intrinsic tumour suppressor mechanism in vivo and in vitro. However, senescent cells display also what has been named as a "Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype" or SASP, which mediates both anti- and pro-tumourigenic properties in neighbouring cells.
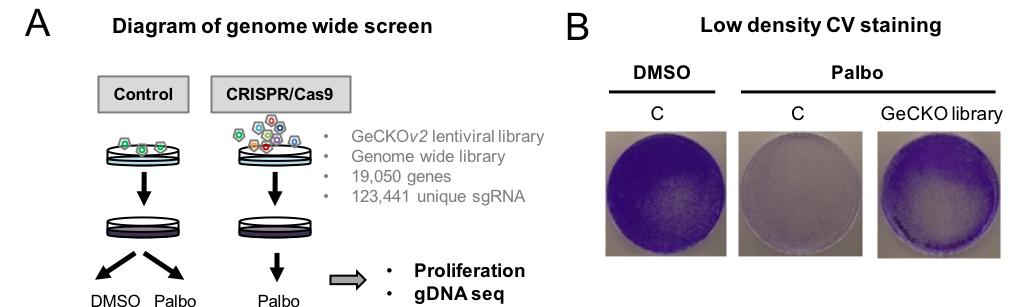
During this last decade, the development of prosenescence therapies has become an attractive strategy as cellular senescence acts as a barrier against tumour progression. In this context, CDK4/6 inhibitors induce senescence and reduce tumour growth in breast cancer patients. However, even though cancer cells are arrested after CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment, genes regulating senescence in this context are still unknown limiting their antitumour activity. For this reason, we have performed a functional genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 genetic screen to identify genes preventing the activation of senescence induced by CDK4/6 inhibitors ().
Following this approach, our lab has identified two genes implicated in the coagulation pathway - the coagulation factor IX (F9) and Protein Z Vitamin K Dependent Plasma Glycoprotein (PROZ) - whose loss prevent the induction of senescence. We believe these markers could be used to predict patient response to CDK4/6 inhibitors improving the efficacy of cancer treatments and overall disease outcome (Cell Death Dis 2022).