The group of Dr. Joaquin Teixidó at the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas has unveiled the molecular mechanism of a novel escape signaling route that melanoma cells use to proliferate and acquire resistance. The work, published in Cancer Research, counted on the collaboration of Dr. Azucena Esparís at Centro de Investigación del Cáncer (Salamanca).
The BRAF V600E mutation is the most prevalent alteration in malignant melanoma, and represented the focus for the development of BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi), which have provided substantial benefits for patients with metastatic melanoma, especially when combined with MEK1/2 inhibitors (MEKi). However, the emergence of resistance represents an important clinical challenge. Frequent mechanisms involved in MAPK inhibitor resistance of melanoma converge in the reactivation of the BRAF-MEK-ERK pathway. Targeting ERK is a suitable strategy currently being investigated in melanoma and other cancers. An advantage for targeting ERK is based on the fact that resistance to BRAFi or MEKi frequently involves the relief of negative feedback mechanisms causing Erk1/2-dependent MAPK pathway re-activation.
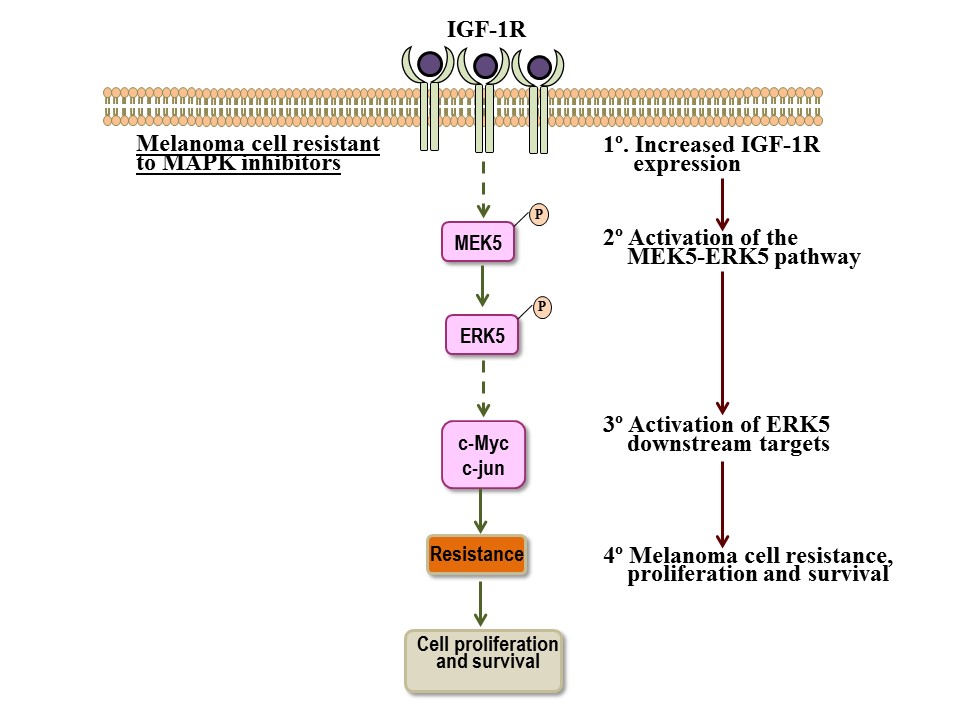
Lucia Benito-Jardón et al. have addressed the possible resistance to ERK inhibitors (ERKi), using SCH772984 (SCH) as a model ERKi to characterize resistance mechanisms in different BRAF V600E melanoma cells. They have found that ERKi-resistant cells were also resistant to combined treatment with BRAFi and MEKi. Resistance to SCH and to BRAFi and MEKi involved stimulation of the IGF-1R-MEK5-Erk5 signaling pathway, which counteracted inhibition of Erk1/2 activation and cell growth. Inhibition of the IGF-1R with linsitinib blocked Erk5 activation in SCH-resistant cells as well as in cells double-resistant to BRAFi and MEKi, and decreased their growth in 3D spheroid growth assays as well as in NOD scid gamma mice. Cells double resistant to BRAFi and MEKi also exhibited downregulated Erk1/2 activation linked to stimulation of the IGF-1R-MEK5-Erk5 pathway, which accounted for resistance.
These data reveal an escape signaling route that melanoma cells use to bypass Erk1/2 blockade during targeted melanoma treatment and offer several possible targets whose disruption may circumvent resistance.
Reference: Resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma involves activation of the IGF-1R-MEK5-Erk5 pathway. Lucía Benito-Jardón, Marta Díaz-Martínez, Nohemi Arellano-Sánchez, Paloma Vaquero-Morales, Azucena Esparís-Ogando and Joaquín Teixidó. Cancer Res March 4, 2019; DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2762. PMID: 30833419

