An international study with the participation of Prof. Guillermo Giménez Gallego and the NMR group at the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas (CSIC), has been published in Cell Reports.
This study contains the discovery and determination of the atomic structure, by NMR spectroscopy, of the protein EPI-X4. This protein prevents that the CXCL12 cytokine interacts with the protein CXCR4, itsr eceptor in the cellular membrane. The knowledge of atomic structure of EPI‑X4 has allowed designing analogues which are one hundred times more potent and can serve as therapeutic agents to treat very important diseases, since the high levels of CXCL12 are associated to inflammations which are difficult to treat,as well as to tumor metastasis. On the other hand, EPI-X4 and the analogues described in the paper inhibit the infection of the X4VIH-1 virus, which is the variety predominant in HIV patients from the moment they start to show symptoms,because the virus requires to bind CXCR4 to invade the cell. Moreover, EPI‑X4 is present abundantly in the urine of patients which suffer from inflammatory kidney diseases, which might allow its use as a marker to diagnose these diseases.
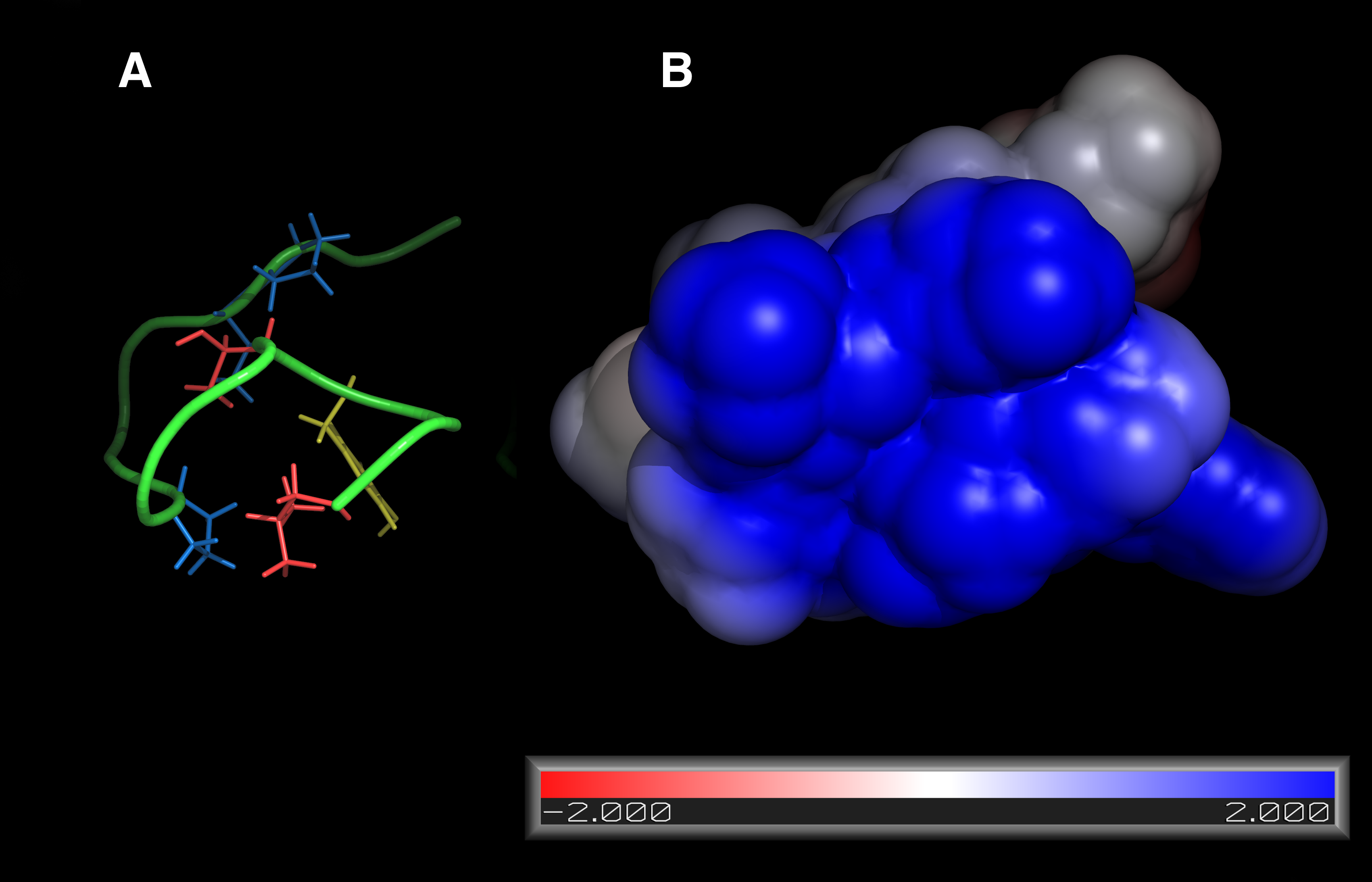
The atomic structure of EPI‑X4 adopts a ring-type disposition with a “tail”. The ring shows a strongly hydrophobic surface as well as one with high density of positive charges, capable to interact with high affinity with the extracellular region of CXCR4, which is extraordinarily abundant in negative charges.

